Book a FREE 15-Minute consultation with our Care Coordinator - Click Here

Mental health,
built around you.
Support your emotional well-being through individual, couples, or family therapy, led by an expert provider who's focused on your needs.
Why Family Time Centers

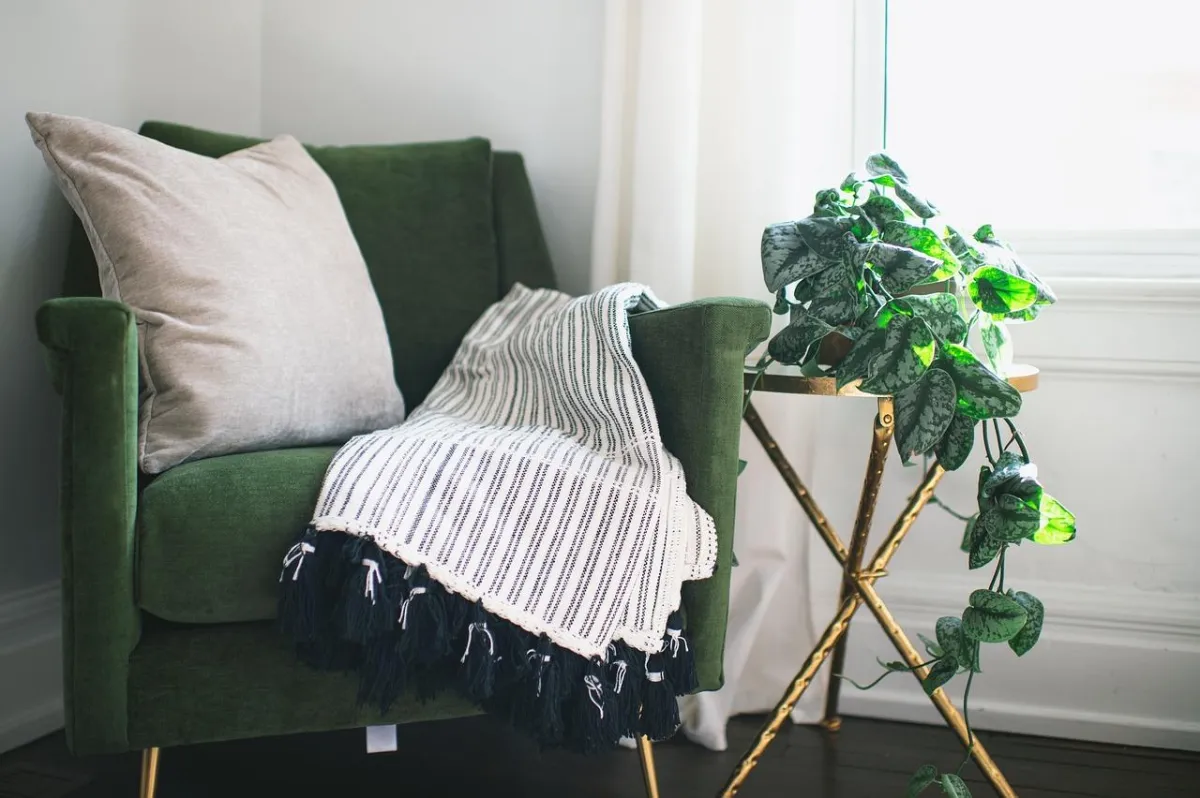
Real Human Connection
We believe in the power of people over technology. Find a therapist who makes you feel safe and empowered.

Matched to Your Needs
Our therapy teams have a broad range of backgrounds and specialty areas, so you can find the right expert for you.

Grounded in Science
We use evidence-based approaches that are proven to help you feel better, faster.
Focused on Results
76% of Octave clients with clinical depression see significant improvement in their symptoms within 12 weeks of care.
Meet Some of our
Team Members
Our team has a wide variety of specialties, backgrounds, and personalities, so we can find the right match for you, based on your unique needs and situation.

FamilyTime Center Clients
"FamilyTime Centers have been a lifesaver. The seamless transition from initial consultation to personalized care has been incredible. Our family feels supported every step of the way."
"The intake process at FamilyTime Centers was smooth and thoughtful. The ease of dealing with insurance and receiving such comprehensive therapy has been a revelation. I can't recommend FamilyTime Centers enough."
"FamilyTime Centers have been a lifesaver. The seamless transition from initial consultation to personalized care has been incredible. Our family feels supported every step of the way."
Stay in touch.
Sign up to receive Family time canter updates and information about mental health tips




If you or someone you know is experiencing an emergency or crisis and needs immediate help, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
© 2025 FamilyTime Center





